Spring-AOP
从源码分析了Spring AOP的实现逻辑,以及利用arthas对代理class进行反编译以更加清晰的理解源码流程
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
其主要功能是向容器中注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这个BeanDefinition,以此实现基于以下注解的代理功能
| 注解名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
@Aspect |
声明一个类是切面类 |
@Before |
前置通知,目标方法执行前执行 |
@After |
后置通知,目标方法执行后执行(无论是否异常) |
@AfterReturning |
返回通知,目标方法正常返回后执行 |
@AfterThrowing |
异常通知,目标方法抛出异常时执行 |
@Around |
环绕通知,完全控制目标方法执行的时机,可决定是否继续执行目标方法 |
@Pointcut |
定义可复用的切点表达式,供上述注解引用 |
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
Spring实现自动装配动态代理的Bean后置处理器,具有最高的执行优先级(表示是最先被执行的BeanPostProcessor。设置最高优先级的代码在org.springframework.aop.config.AopConfigUtils#registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired中)
wrapIfNecessary
bean进行包装(增强)的入口,它会在如下两个地方被调用
- postProcessAfterInitialization:常规的的bean初始化完成后hook,需要对bean进行代理并返回给容器
- getEarlyBeanReference:针对循环依赖需要提前获取bean的引用。Spring 会在三级缓存中暴露“早期对象引用”。如果此 bean 需要 AOP,必须在这个阶段就包上代理,否则依赖方会拿到原始对象,导致切面失效。
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 已经处理过
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
// 无需增强的bean缓存判断
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
// 是一个基础设施类或者指定的不需要代理
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 查找这个bean能使用的所有Advisor
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { // 存在增强器
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 创建其代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
// 当前bean不需要增强,缓存起来
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
获取Advisor阶段
首先Advisor是什么?
我理解为增强器,一个Advisor对应一个切面。既包含Advice,也包含过滤器(判断bean是否需要增强的东西)。所以能用一个Advisor来判断任意一个bean是否能被它增强,并提供增强的Advice。
主要子接口为PointcutAdvisor,PointcutAdvisor提供了Pointcut,利用这个Pointcut即可以bean的class和method进行匹配看它是否能被增强。而Advisor获取的Advice则为真正执行代理方法的拦截器。
findCandidateAdvisors
有两种如下获取Advisor的方式
查找所有实现了Advisor接口的BeanDefinition,并对其进行实例化(这种一般都是框架注册的增强器)
注解方式:获取所有基于注解的切面bean,并进行实例化
先拿到容器中所有Bean的beanName,再遍历这些beanName。通过BeanFactory获取当前beanName的Class,再判断Class上是否有@Aspect注解。如果存在@Aspect,就利用ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory去解析这些Bean,将@Aspect Bean中的每个增强方法(如下注解,每个注解标注的方法就是一个增强方法)构造成一个Advisor(实现类为InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl),最后封装到List
里,返回给上层
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// 查找spring内置的增强器(包括不限于事务、缓存等)
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// aspectJAdvisorsBuilder不会为空,默认为BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilderAdapter
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
// 获取所有的与@Aspect注解相关的Advisor
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}
// 父类中的findAdvisorBeans
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
// 先从缓存中找,没有再搜索
String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;
if (advisorNames == null) { // 缓存为空
// 查找出所有实现了Advisor接口的BeanDefinition,并缓存
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
if (advisorNames.length == 0) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : advisorNames) {
if (isEligibleBean(name)) {
if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'");
}
} else {
try {
// 尝试实例化这个Advisor Bean,并放入结果中
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
} catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause();
if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) {
BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause;
String bceBeanName = bce.getBeanName();
if (bceBeanName != null && this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bceBeanName)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Skipping advisor '" + name +
"' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage());
}
// Ignore: indicates a reference back to the bean we're trying to advise.
// We want to find advisors other than the currently created bean itself.
continue;
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
return advisors;
}
// BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder#buildAspectJAdvisors方法,找出基于注解的切面
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
// @Aspect注解BeanName的缓存
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取所有beanName
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// 获取这个bean的type
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 存在 org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect 注解
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
// 解析@Aspetc的value值,如果没有,默认kind就为SINGLETON
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(
this.beanFactory, beanName);
// 解析标记 AspectJ 注解中的增强方法,并将每个切点方法都构造成一个Advisor
// 其实现类为InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
// 缓存起来切面的解析结果
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
} else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
} else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(
this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) { // 没有自定义的@Aspect,返回空
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
} else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}
findAdvisorsThatCanApply
将上面流程中获取到的所有Advisor做过滤,过滤出可以对当前bean进行增强的Advisor。核心方法在org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils#canApply中
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) { // 先按类匹配,如果类都匹配不了,那直接就不需要代理了
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher(); // 获取方法匹配器
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
// 目标类和其所有接口的集和
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
// 对目标类和其所有接口的每个方法都进行匹配,只要能匹配上,就代表这个类可以增强,直接返回true
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null
? introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)
: methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
sortAdvisors
源码就不分析了,直接说作用:它是 Spring AOP 中对多个 Advisor(增强器)进行排序的关键逻辑。它根据切面、通知类上的 @Order 注解或实现 Ordered 接口的优先级,对同一目标类或方法的所有 Advisor 进行排序。
排序完成后,每个类或方法的增强器顺序就被固定下来。在运行时调用该方法时,AOP 拦截器链会严格按照这个顺序执行对应的切面逻辑,确保增强行为的预期一致性。
开始增强(创建代理)
cglib getProxy
cglib的增强实现主要步骤总结
校验final方法(只是打个日志,final方法不能增强)
创建org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer(核心的cglib增强器)
对Enhancer进行一系列的填充,包括设置当前Class为增强类的父类。当前Class的所有接口,增强类也要实现。
设置增强Class的命名策略(BySpringCGLIB)
默认再将当前线程上下文的ClassLoader设为加载增强Class字节码的ClassLoader
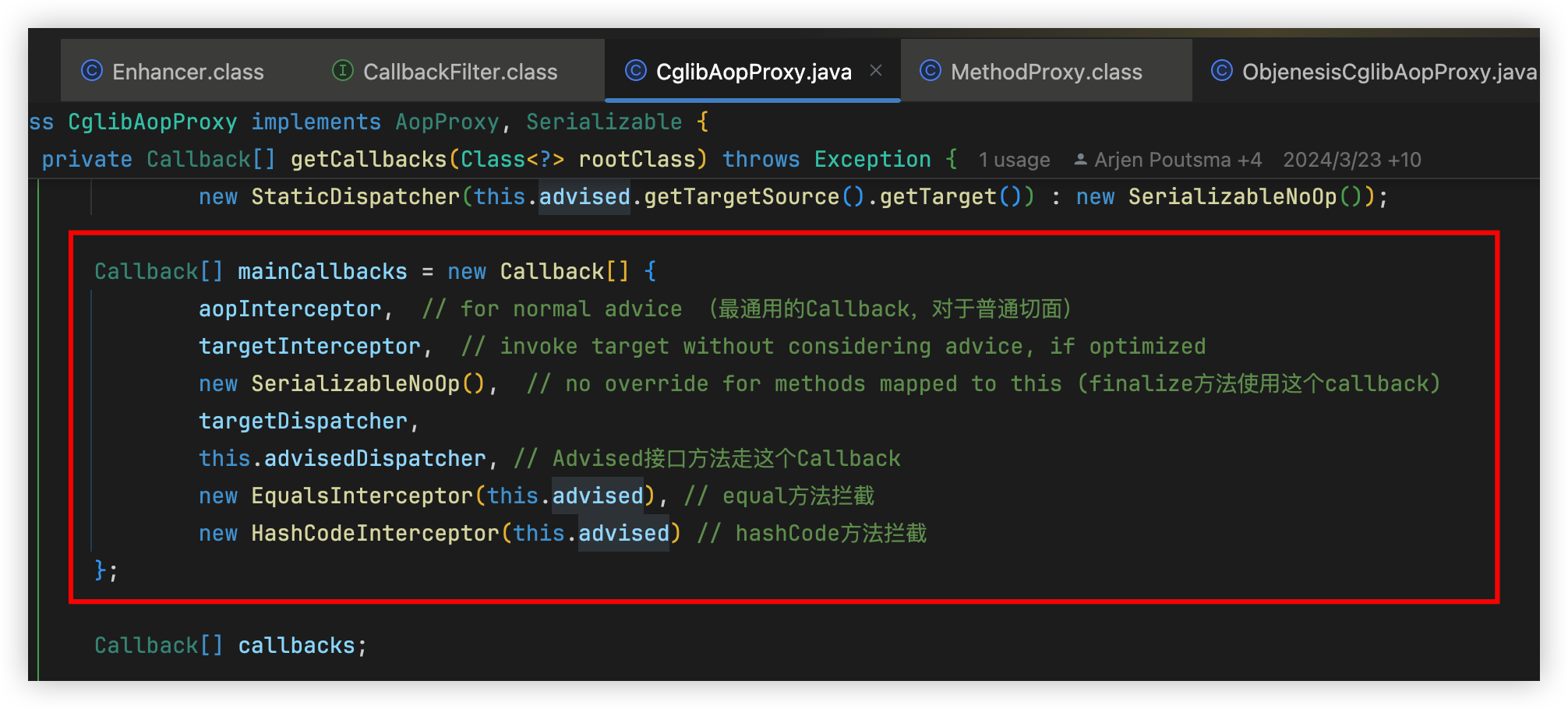
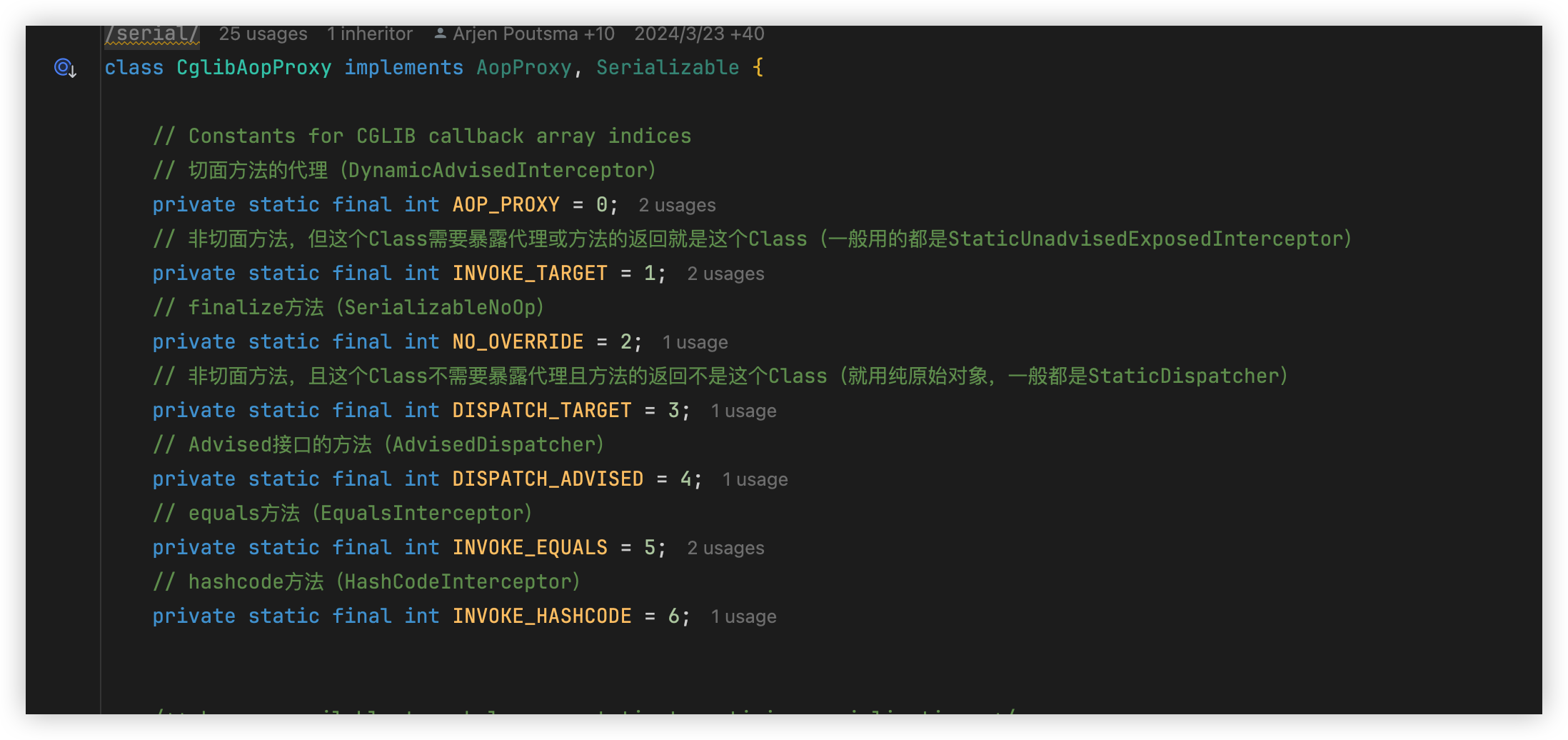
对Enhancer设置一些Callback,并设置固定的CallbackFilter(ProxyCallbackFilter)。非常重要:
Callback数组(每一个Callback都是方法的拦截器)
Callback数组的索引(ProxyCallbackFilter#accept实现),用来确定被增强的类的每一个方法该使用具体的某个拦截器,返回的是拦截器的数组索引
生成增强Class的字节码并实例化(代理bean就产生了),将其返回
// CglibAopProxy的创建代理方法
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
// 上一个被代理的目标类class(有可能已经是cglib的代理类了)
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
// 真正代理的目标类class
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) { // 已经是个cglib代理类了,就需要把真正被代理类的class和接口找出来
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// 验证class的final相关方法并写日志
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// 创建通用的增强器,准备增强了
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
// 设置被代理类class为增强类的父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
// 对增强类设置接口:Advised和SpringProxy
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader));
// 设置拦截器(真正支持切面操作的拦截器)
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// 非常重要,就是通过这个filter来确定某个方法应该使用哪一个Callback的
// 所以,代理类的任何一个方法只会用上一个Callback
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// 生成代理类的class并实例化其对象
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
} catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
jdk getProxy
// JdkDynamicAopProxy的创建代理方法,该代理的InvocationHandler就为JdkDynamicAopProxy本身
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
// 对增强类设置Interface:Advised和SpringProxy和DecoratingProxy
Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
}
调用阶段
cglib invoke
cglib代理类中方法有切面时的调用重点流程分析(这时使用的Callback就是DynamicAdvisedInterceptor)
获取方法对应的拦截器链
Spring 会调用
AdvisorChainFactory#getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice方法,为当前方法构建拦截器链。
它会遍历所有注册的Advisor,并依次通过其中的ClassFilter和MethodMatcher判断当前方法是否匹配。如果匹配,就将该Advisor对应的拦截器(MethodInterceptor)加入到列表中,并最终缓存该方法与其拦截器链的映射关系。触发代理方法调用
如果目标类采用了 CGLIB 代理(
proxyTargetClass = true),则在调用代理对象方法时,会进入CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept方法。构造并执行拦截链
Spring 会构造一个
CglibMethodInvocation对象,它是ReflectiveMethodInvocation的子类,封装了目标对象、方法、参数、拦截器链等执行上下文。
调用proceed()方法开始执行拦截链。依次执行拦截器
proceed()方法会通过内部字段currentInterceptorIndex(初始值为 -1)递增索引,按顺序执行拦截器链中的下一个MethodInterceptor。
每个拦截器如果调用了invocation.proceed(),则控制权会继续传递给下一个拦截器,实现“链式调用”。执行原始方法
当所有拦截器都执行完后(即
currentInterceptorIndex >= interceptors.size()),会最终调用原始目标对象的实际方法,实现增强与目标方法的结合。
// DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept的入口
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
// 先准备目标对象源(调用原bean方法时会用到)
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// 在当前线程上下文中设置了需要暴露代理,就要设置到当前线程ThreadLocal中
// 就是用来解决方法内部需要调用代理方法
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// 获取真实的,不是代理的目标对象
// 例:Session域从SimpleBeanTargetSource中获取,再转到BeanFactory,再转到SessionScope中,获取目标对象
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// 对当前方法构造切面链并缓存
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// 无切面,且方法为public,直接调用原方法
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
} else { // 存在切面,构造方法调用器并执行
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
} finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) { // 方法代理全部执行完毕,恢复执行前的现场
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
jdk invoke
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
// 一些通用方法的处理
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
return equals(args[0]);
} else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
return hashCode();
} else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
// opaque为false,且该方法的类为实现了Advised的接口,则使用advised字段调用该方法
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { // 需要暴露当前proxy,以便在本类中调用代理方法
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// 获取这个方法的所有拦截链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
if (chain.isEmpty()) { // 拦截链为空,则直接调用原方法
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
} else {
// 构造ReflectiveMethodInvocation,准备走代理方法了
MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass,
chain);
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// 处理返回值类型
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
retVal = proxy;
} else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
} finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// 恢复现场,移除当前线程上下文中的proxy
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
ReflectiveMethodInvocation
Spring AOP 的cglib和jdk代理都会用到的数据结构。是 方法拦截链执行的核心实现类。每当调用代理类中的方法时,都会构造一个ReflectiveMethodInvocation对象,内部封装了一个方法调用的上下文,包括目标对象、目标方法、方法参数、拦截器链等。核心是通过调用 proceed() 方法按顺序执行所有拦截器,最终调用目标方法。
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable {
// 用于记录当前执行到第几个拦截器
private int currentInterceptorIndex = -1;
// 进行动态增强器的匹配判断,执行拦截器,和传播的实现
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// 执行完所有增强方法后执行切点方法
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
// 获取下一个要执行的拦截器
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers
.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
// 调用拦截器方法时,都需要将this作为参数传递以保证当前拦截能传播给后面的增强器(proceed方法)
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) { // 动态匹配的增强器,需要进行动态参数匹配
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
// 匹配,执行拦截器
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
} else {
// 匹配失败就不执行拦截器,触发下一个拦截器的判断和执行
return proceed();
}
} else {
// 非动态拦截器,比如事务的TransactionInterceptor,和异步的 AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor等等
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
}
总结
不论是cglib还是jdk的增强,增强的实现都可以总结为对原方法可使用的Advisor的收集,再构造成ReflectiveMethodInvocation,由ReflectiveMethodInvocation去进行动态增强器(一般都和参数有关)的判断,执行拦截器和拦截的传播。
且Spring都会默认对代理bean实现两个接口(代码实现在AopProxyUtils#completeProxiedInterfaces中),分别是SpringProxy和Advised。SpringProxy用来表示当前bean已经被spring的增强了,而Advised则可以用来拿到原始bean(所以,要在代理bean中拿到原始bean,直接将代理bean强转为Advised,再利用其getTargetSource方法得到原始非代理bean)
AOP测试
被增强的class,其中@BizLog是注解切面,切面类为LogInterceptor,用来做日志打印的
package site.shanzhao;
import site.shanzhao.BizLog;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Component
public class SpringAopDemo {
@Transactional
@BizLog
public void aopMethod(){
System.out.println("aopMethod run...............");
}
public void notAopMethod(){
System.out.println("notAopMethod run...............");
}
}
arthas解密
sc
sc -d site.shanzhao.SpringAopDemo:查看指定的class加载信息(这里有两个class信息,增强class和源class,我这里只关心增强的class)
重点观察interfaces这一行,可以发现这个代理类实现了3个接口,分别为SpringProxy,Advised和Factory
class-info site.shanzhao.SpringAopDemo$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6d7e1f60
code-source /Users/shanzhao/IdeaProjects/soil/target/classes/
name site.shanzhao.SpringAopDemo$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6d7e1f60
isInterface false
isAnnotation false
isEnum false
isAnonymousClass false
isArray false
isLocalClass false
isMemberClass false
isPrimitive false
isSynthetic false
simple-name SpringAopDemo$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6d7e1f60
modifier public
annotation
interfaces org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy,org.springframework.aop.framework.Advised,org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Factory
super-class +-site.shanzhao.SpringAopDemo
+-java.lang.Object
class-loader +-sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
+-sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@13fee20c
classLoaderHash 18b4aac2
jad
- jad site.shanzhao.SpringAopDemo$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6d7e1f60:使用jad反编译代理class,这里只展示出了重点代码
// package site.shanzhao;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice;
import org.springframework.aop.Advisor;
import org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy;
import org.springframework.aop.TargetClassAware;
import org.springframework.aop.TargetSource;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.Advised;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.AopConfigException;
import org.springframework.cglib.core.ReflectUtils;
import org.springframework.cglib.core.Signature;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Callback;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Dispatcher;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Factory;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.NoOp;
import site.shanzhao.SpringAopDemo;
public class SpringAopDemo$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6d7e1f60
extends SpringAopDemo
implements SpringProxy,
Advised,
Factory {
private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;
public static Object CGLIB$FACTORY_DATA;
private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;
private static final Callback[] CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_1;
private NoOp CGLIB$CALLBACK_2;
private Dispatcher CGLIB$CALLBACK_3;
private Dispatcher CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_5;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_6;
// 为org.springframework.aop.framework.Advised的接口,内部直接使用4号callback转化为ProxyFactory对象再调用目标方法
@Override
public final TargetSource getTargetSource() {
Dispatcher dispatcher = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
if (dispatcher == null) {
SpringAopDemo$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6d7e1f60.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
dispatcher = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_4;
}
return ((Advised) dispatcher.loadObject()).getTargetSource();
}
// aop增强的方法,使用0号callback进行处理,实现类为DynamicAdvisedInterceptor。
// 应该有两个适合这个方法的Advisor,一个是@BizLog的LogInterceptor切面,另一个是事物切面
public final void aopMethod() {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
SpringAopDemo$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6d7e1f60.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
Object object = methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$aopMethod$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs,
CGLIB$aopMethod$0$Proxy);
return;
}
super.aopMethod();
}
// 未增强的方法,同样使用0号callback进行处理,但却不会有适合这个方法的Advisor
public final void notAopMethod() {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
SpringAopDemo$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6d7e1f60.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
Object object = methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$notAopMethod$1$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs,
CGLIB$notAopMethod$1$Proxy);
return;
}
super.notAopMethod();
}
// Object的equals方法,使用5号callback处理,实现类为EqualsInterceptor
public final boolean equals(Object object) {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_5;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
SpringAopDemo$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$6d7e1f60.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_5;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
Object object2 = methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$equals$2$Method, new Object[] { object },
CGLIB$equals$2$Proxy);
return object2 == null ? false : (Boolean) object2;
}
return super.equals(object);
}
}
debug下代理类的信息
这是从容器中直接获取SpringAopDemo这个class得到的对象,也就是代理类而不是源对象
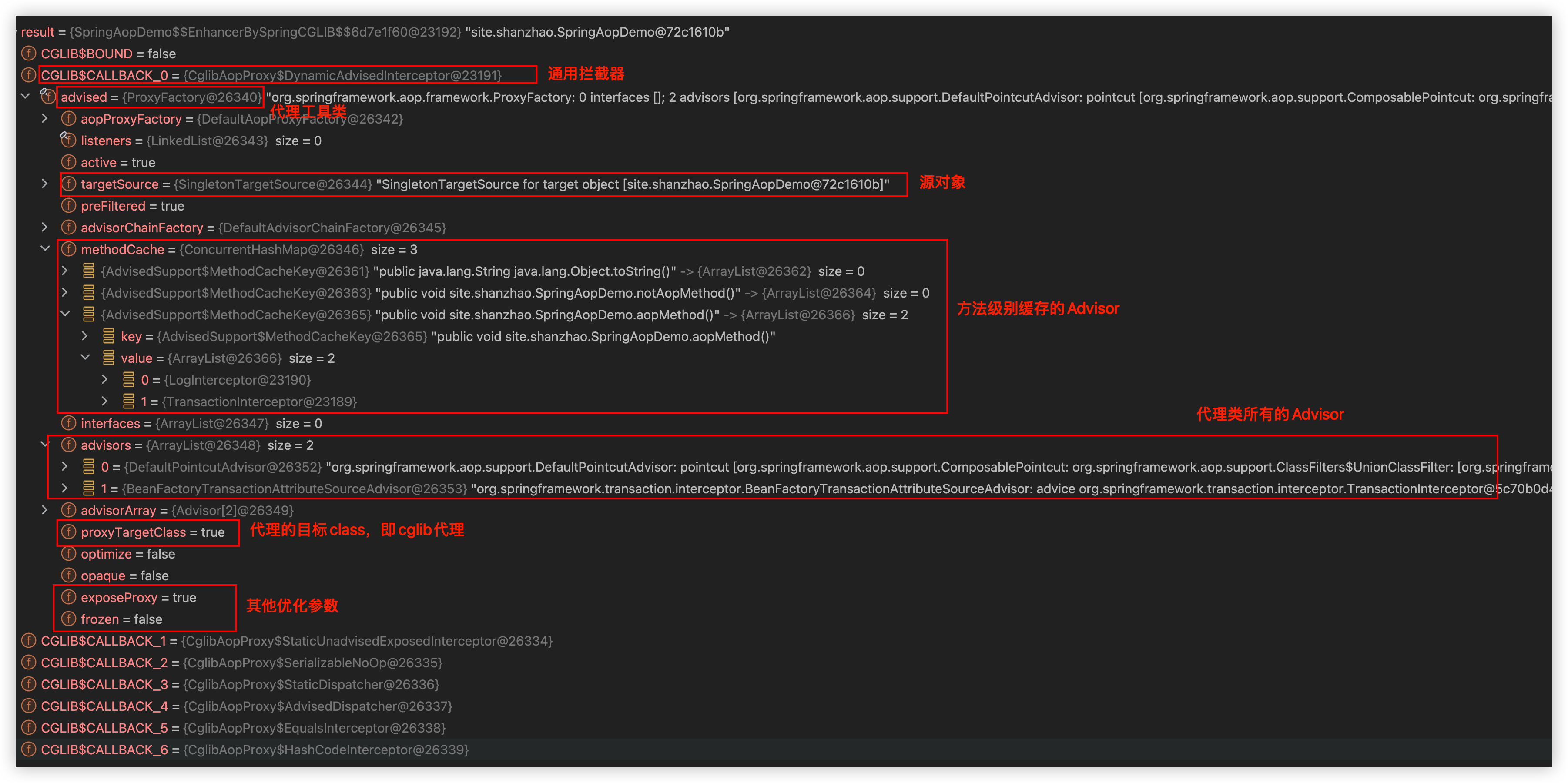
重点信息已用红框框处,逐个分析
- CGLIB$CALLBACK_0:通用拦截器,有切面和没有切面的普通方法方法都会用
- advised:实现为org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory。是 Spring AOP 中封装代理创建逻辑的核心工具类,实现了
Advised接口。它通过维护一系列配置和内部结构,完成对目标对象的方法级别增强。- targetSource:内部封装了源对象,可以将当前代理类强转为Advised,在调用其getTargetSource方法获取到源对象
- methodCache:缓存方法与其对应增强(Advisor)链的映射,加快方法调用时的拦截查找过程。
- notAopMethod:没有切面,所以size=0
- aopMethod:有两个切面,缓存的size=2
- advisor:代理类所有的Advisor
- proxyTargetClass:是否直接代理的目标class。为true则表示cglib proxy,fasle则是jdk proxy
- exposeProxy:是否将当前代理暴露到
ThreadLocal上下文中,允许在目标对象内部通过AopContext.currentProxy()获取自身代理对象,用于内部方法调用也能被增强。 - frozen:表示配置是否被冻结。默认为false,支持在运行时动态添加或移除
Advisor。如果设置为true,配置将被锁定,并跳过methodCache的清理逻辑以提升性能。