SpringBoot(四) — Condition相关原理
基于Spring Boot 2.7.x 版本,深入分析了OnBean、OnClass、OnProperty这三类常见Condition的源码实现,在此基础上,探讨了 @Conditional 注解的组合用法(与、或、非逻辑)的处理机制。
同时,分析了Condition匹配结果的debug支持实现,以及 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 中Condition判断的触发流程,重点关注其通过 importedBy 链支持的 TrackedConditionEvaluator 回溯与剪枝优化策略
最后,提供了逻辑或@Conditional组合与 importedBy路径 skip 判定的测试用例,以验证整体逻辑的正确性
Conditional注解
项目中常用的@ConditionalOnBean,@ConditionalOnClass,@ConditionalOnProperty等注解都有一个共同的元注解@Conditional,Spring通过这个元注解@Conditional中指定的Condition类来判断某个配置类或Bean 是否应该被加载。Condition接口定义如下
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Condition {
boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
}
其中参数作用如下:
- ConditionContext:提供**
Condition评估所需的上下文环境**。包括BeanFactory,BeanDefinitionRegistry和Environment等组件 - AnnotatedTypeMetadata:当前@Conditional所标注的类或方法上的所有注解元信息
我这里只分析了常用的bean,properties,和class相关的Condition。套路都一样,剩下的可自行分析
OnBeanCondition
是@ConditionalOnBean、@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate、@ConditionalOnMissingBean专用的Condition实现类,核心作用是根据注解中指定的 type / name / annotation 等参数,判断当前容器中是否存在匹配的 Bean,并根据注解功能来解析结果
Spec
是对上述三个注解的统一解析封装结构,用于抽象出注解中的条件信息,每一个配置类或方法上存在的相关注解,最终都会被解析为一个 Spec 实例,其具体参数如下
private static class Spec<A extends Annotation> {
private final ClassLoader classLoader;
private final Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType;
private final Set<String> names;
private final Set<String> types;
private final Set<String> annotations;
private final Set<String> ignoredTypes;
private final Set<Class<?>> parameterizedContainers;
private final SearchStrategy strategy;
Spec(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, MergedAnnotations annotations,
Class<A> annotationType) {
MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes = annotations.stream(annotationType)
.filter(MergedAnnotationPredicates.unique(MergedAnnotation::getMetaTypes))
.collect(MergedAnnotationCollectors.toMultiValueMap(Adapt.CLASS_TO_STRING));
MergedAnnotation<A> annotation = annotations.get(annotationType);
this.classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
this.annotationType = annotationType;
// name属性解析,即beanName
this.names = extract(attributes, "name");
// annotation属性,即bean上的注解
this.annotations = extract(attributes, "annotation");
this.ignoredTypes = extract(attributes, "ignored", "ignoredType");
this.parameterizedContainers = resolveWhenPossible(extract(attributes, "parameterizedContainer"));
this.strategy = annotation.getValue("search", SearchStrategy.class).orElse(null);
// value和type解析,即bean class
Set<String> types = extractTypes(attributes);
BeanTypeDeductionException deductionException = null;
// 未配置value和type时,对@Bean方法使用其returnType作为types
if (types.isEmpty() && this.names.isEmpty()) {
try {
types = deducedBeanType(context, metadata);
} catch (BeanTypeDeductionException ex) {
deductionException = ex;
}
}
this.types = types;
// 校验types,names,annotations至少要有存在一个
validate(deductionException);
}
}
MatchResult
表示某个 Spec 在指定容器上下文中的匹配结果,不同类型的注解会根据自身定义对 MatchResult 的结果进行判断,来决定是否匹配成功
private static final class MatchResult {
/**
* annotation对应的bean集合(在容器里)
*/
private final Map<String, Collection<String>> matchedAnnotations = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 在容器里的beanName
*/
private final List<String> matchedNames = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* type对应的bean集合(在容器里)
*/
private final Map<String, Collection<String>> matchedTypes = new HashMap<>();
/**
* annotation对应的bean不在容器中
*/
private final List<String> unmatchedAnnotations = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* beanName对应的bean不在容器中
*/
private final List<String> unmatchedNames = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* type对应的bean不在容器中
*/
private final List<String> unmatchedTypes = new ArrayList<>();
private final Set<String> namesOfAllMatches = new HashSet<>();
}
getMatchingBeans
getMatchingBeans是根据 Spec 提供的条件,在容器里找出符合要求 Bean 的核心方法。可通过如下代码总结出OnBeanCondition支持的核心匹配能力包括:
- 按type、beanName、annotation搜索对应的bean是否存在
- 支持搜索父容器(SpringCloud中存在)
- 支持泛型
- 支持忽略指定type的bean(等价于搜索结果会remove掉这些ignoreType的bean)
protected final MatchResult getMatchingBeans(ConditionContext context, Spec<?> spec) {
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 父容器搜索判断(比如SpringCloud环境下存在父容器)
boolean considerHierarchy = spec.getStrategy() != SearchStrategy.CURRENT;
// 泛型判断支持(示例:@ConditionalOnMissingFilterBean)
Set<Class<?>> parameterizedContainers = spec.getParameterizedContainers();
if (spec.getStrategy() == SearchStrategy.ANCESTORS) {
BeanFactory parent = beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory();
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory.class, parent,
"Unable to use SearchStrategy.ANCESTORS");
beanFactory = (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) parent;
}
// 匹配结果
MatchResult result = new MatchResult();
// 获取需要被忽略的bean的beanName
Set<String> beansIgnoredByType = getNamesOfBeansIgnoredByType(classLoader, beanFactory, considerHierarchy,
spec.getIgnoredTypes(), parameterizedContainers);
// ----------------- 处理类型匹配部分 ------------------
for (String type : spec.getTypes()) {
// 获取类型对应的beanName
Collection<String> typeMatches = getBeanNamesForType(classLoader, considerHierarchy, beanFactory, type,
parameterizedContainers);
// 移除被忽略的 Bean 以及scope的代理bean
typeMatches.removeIf((match) -> beansIgnoredByType.contains(match) || ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(match));
if (typeMatches.isEmpty()) { // type过滤后没有对应的bean在容器中,记录为不匹配
result.recordUnmatchedType(type);
} else {
result.recordMatchedType(type, typeMatches);
}
}
// ----------------- 处理注解匹配部分 ------------------
for (String annotation : spec.getAnnotations()) {
// 获取被指定注解标记的beanName
Set<String> annotationMatches = getBeanNamesForAnnotation(classLoader, beanFactory, annotation,
considerHierarchy);
// 移除掉被忽略的 bean
annotationMatches.removeAll(beansIgnoredByType);
if (annotationMatches.isEmpty()) {// annotation过滤后没有对应的bean在容器中,记录为不匹配
result.recordUnmatchedAnnotation(annotation);
} else {
result.recordMatchedAnnotation(annotation, annotationMatches);
}
}
// ----------------- 处理按beanName匹配部分 ------------------
for (String beanName : spec.getNames()) {
if (!beansIgnoredByType.contains(beanName) && containsBean(beanFactory, beanName, considerHierarchy)) {
// 没被忽略,切在容器中存在这个beanName。匹配命中
result.recordMatchedName(beanName);
} else { // 匹配失败
result.recordUnmatchedName(beanName);
}
}
return result;
}
getMatchOutcome
getMatchOutcome会拿 Spec 的匹配结果,结合具体是哪种 @ConditionalOn* 注解,来决定条件是否满足。我这里对getMatchOutcome方法按注解拆分一下,不影响其逻辑
@ConditionalOnBean
要求所有指定的参数都必须存在对应的bean(即全匹配)。如果有任意一个参数没有对应的bean存在于指定容器中,则不匹配,返回noMatch
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty();
MergedAnnotations annotations = metadata.getAnnotations();
if (annotations.isPresent(ConditionalOnBean.class)) {
Spec<ConditionalOnBean> spec = new Spec<>(context, metadata, annotations, ConditionalOnBean.class);
// 进行匹配
MatchResult matchResult = getMatchingBeans(context, spec);
if (!matchResult.isAllMatched()) { // 任意一个条件没匹配到bean,则返回noMatch
String reason = createOnBeanNoMatchReason(matchResult);
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(spec.message().because(reason));
}
matchMessage = spec.message(matchMessage)
.found("bean", "beans")
.items(Style.QUOTE, matchResult.getNamesOfAllMatches());
}
// matched
return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage);
}
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate
校验指定参数对应的bean在容器中只存在一个bean或一个primary bean,所以@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate的参数也是单个的,仅支持type匹配
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty();
MergedAnnotations annotations = metadata.getAnnotations();
if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class.getName())) {
Spec<ConditionalOnSingleCandidate> spec = new SingleCandidateSpec(context, metadata, annotations);
MatchResult matchResult = getMatchingBeans(context, spec);
if (!matchResult.isAllMatched()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(spec.message().didNotFind("any beans").atAll());
}
Set<String> allBeans = matchResult.getNamesOfAllMatches();
if (allBeans.size() == 1) { // 只匹配到一个bean,则matched
matchMessage = spec.message(matchMessage).found("a single bean").items(Style.QUOTE, allBeans);
} else {
// 多个bean,再校验是否只有一个primary bean
List<String> primaryBeans = getPrimaryBeans(context.getBeanFactory(), allBeans,
spec.getStrategy() == SearchStrategy.ALL);
if (primaryBeans.isEmpty()) {
return ConditionOutcome
.noMatch(spec.message().didNotFind("a primary bean from beans").items(Style.QUOTE, allBeans));
}
if (primaryBeans.size() > 1) {
return ConditionOutcome
.noMatch(spec.message().found("multiple primary beans").items(Style.QUOTE, primaryBeans));
}
matchMessage = spec.message(matchMessage)
.found("a single primary bean '" + primaryBeans.get(0) + "' from beans")
.items(Style.QUOTE, allBeans);
}
}
// matched
return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage);
}
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
和@ConditionalOnBean完全相反,所有参数都不能存在对应的bean在指定容器里(全不匹配)才matched
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty();
MergedAnnotations annotations = metadata.getAnnotations();
// -------------- @ConditionalOnMissingBean 注解处理 --------------
if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class.getName())) {
Spec<ConditionalOnMissingBean> spec = new Spec<>(context, metadata, annotations,
ConditionalOnMissingBean.class);
MatchResult matchResult = getMatchingBeans(context, spec);
if (matchResult.isAnyMatched()) { // 任意一个条件匹配到了bean,apply注解逻辑返回noMatch
String reason = createOnMissingBeanNoMatchReason(matchResult);
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(spec.message().because(reason));
}
matchMessage = spec.message(matchMessage).didNotFind("any beans").atAll();
}
// matched
return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage);
}
OnClassCondition
被@ConditionalOnClass和@ConditionalOnMissingClass使用,用来判断指定的class是否存在于指定ClassLoader的classpath里
ClassNameFilter
两个Filter,PRESENT和MISSING,内部通过Class#forName方法判断指定的class能否被指定的ClassLoader加载(即在其classpath下)
protected enum ClassNameFilter {
PRESENT {
@Override
public boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) {
return isPresent(className, classLoader);
}
},
MISSING {
@Override
public boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) {
return !isPresent(className, classLoader);
}
};
abstract boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader);
static boolean isPresent(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
try {
// 使用Class.forName检测class是否存在。
if (classLoader != null) {
Class.forName(className, false, classLoader);
} else {
Class.forName(className);
}
return true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 不存的在会抛ClassNotFoundException,被异常捕获返回false
return false;
}
}
}
getMatchOutcome
@ConditionalOnClass
利用ClassNameFilter.MISSING校验指定的class都必须存在
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty();
// 解析@ConditionalOnClass的value和name
List<String> onClasses = getCandidates(metadata, ConditionalOnClass.class);
if (onClasses != null) {
// ClassNameFilter.MISSING过滤器得到的结果表示 在指定ClassLoader下不存在对应的class
List<String> missing = filter(onClasses, ClassNameFilter.MISSING, classLoader);
if (!missing.isEmpty()) { // 任意一个class不存在,不满足@ConditionalOnClass逻辑,返回noMatch
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnClass.class)
.didNotFind("required class", "required classes")
.items(Style.QUOTE, missing));
}
matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnClass.class)
.found("required class", "required classes")
.items(Style.QUOTE, filter(onClasses, ClassNameFilter.PRESENT, classLoader));
}
return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage);
}
@ConditionalOnMissingClass
利用ClassNameFilter.PRESENT校验指定的class都不能存在
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty();
// 解析@ConditionalOnMissingClass的value和name
List<String> onMissingClasses = getCandidates(metadata, ConditionalOnMissingClass.class);
if (onMissingClasses != null) {
// ClassNameFilter.PRESENT过滤器得到的结果表示 在指定ClassLoader下存在对应的class
List<String> present = filter(onMissingClasses, ClassNameFilter.PRESENT, classLoader);
if (!present.isEmpty()) { // 任意一个class存在,不满足@ConditionalOnMissingClass逻辑,返回noMatch
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnMissingClass.class)
.found("unwanted class", "unwanted classes")
.items(Style.QUOTE, present));
}
matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnMissingClass.class)
.didNotFind("unwanted class", "unwanted classes")
.items(Style.QUOTE, filter(onMissingClasses, ClassNameFilter.MISSING, classLoader));
}
return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage);
}
OnPropertyCondition
被@ConditionalOnProperty使用,可根据指定的属性判断是否存在对应的value在Spring的Environment中
Spec
是对@ConditionalOnProperty注解的统一解析封装结构,并通过内部的collectProperties方法进行配置匹配
private static class Spec {
private final String prefix;
private final String havingValue;
private final String[] names;
private final boolean matchIfMissing;
private void collectProperties(PropertyResolver resolver, List<String> missing, List<String> nonMatching) {
for (String name : this.names) {
// 对每个属性添加prefix
String key = this.prefix + name;
if (resolver.containsProperty(key)) {
// 有这个属性,根据value是否匹配校验
if (!isMatch(resolver.getProperty(key), this.havingValue)) {
nonMatching.add(name);
}
} else {
// 没这个属性,则根据matchIfMissing来判断
if (!this.matchIfMissing) {
missing.add(name);
}
}
}
}
private boolean isMatch(String value, String requiredValue) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(requiredValue)) {
return requiredValue.equalsIgnoreCase(value);
}
// havingValue未配值时
return !"false".equalsIgnoreCase(value);
}
}
getMatchOutcome
只关注内部核心determineOutcome方法,并根据其对配置匹配结果的处理,可总结出如下规则(满足任意规则都会返回noMatch):
- 不存在对应配置key时:matchIfMissing=false
- 存在对应配置key时:其value和havingValue不匹配
private ConditionOutcome determineOutcome(AnnotationAttributes annotationAttributes, PropertyResolver resolver) {
Spec spec = new Spec(annotationAttributes);
List<String> missingProperties = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonMatchingProperties = new ArrayList<>();
spec.collectProperties(resolver, missingProperties, nonMatchingProperties);
if (!missingProperties.isEmpty()) {// 没对应的属性,且matchIfMissing=false。返回noMatch
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnProperty.class, spec)
.didNotFind("property", "properties")
.items(Style.QUOTE, missingProperties));
}
if (!nonMatchingProperties.isEmpty()) { // 有对应的属性,但其value不匹配。也返回noMatch
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnProperty.class, spec)
.found("different value in property", "different value in properties")
.items(Style.QUOTE, nonMatchingProperties));
}
return ConditionOutcome
.match(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnProperty.class, spec).because("matched"));
}
Conditional组合
前面介绍的条件注解默认是与逻辑:多个 @Conditional 注解应用在同一个配置类或方法上时,只有全部满足,才会注册对应的 Bean
但在某些场景下,我们可能需要更复杂的组合判断逻辑(任意满足 -> 或,全部不满足 -> 非)。SpringBoot 为此提供了一个通用的组合条件抽象工具:AbstractNestedCondition,并基于它提供了三种常用组合实现
AbstractNestedCondition
这是一个抽象类,SpringBoot 用它来实现条件组合的能力。它的核心逻辑为:
- 查找该当前
Condition类中所有的内部类 - 对内部类上定义的
Condition逐个执行matches匹配 - 收集每个内部类整体的匹配结果(内部类上多个
Condition是与逻辑) - 最终调用模板方法
getFinalMatchOutcome(),由子类决定这些匹配结果是否通过(实现“与”、“或”、“非”逻辑)
需要注意的是在收集某个内部类的ConditionOutcome结果时调用了getUltimateOutcome这个方法,其会对内部类所有的ConditionOutcome做与逻辑判断并返回成一个ConditionOutcome。因此要想实现更细粒度的组合,应将每个Conditional注解拆分到不同的内部类中
public abstract class AbstractNestedCondition extends SpringBootCondition implements ConfigurationCondition {
private final ConfigurationPhase configurationPhase;
@Override
public ConfigurationPhase getConfigurationPhase() {
return this.configurationPhase;
}
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
String className = getClass().getName();
// 构造内部条件集合(每个内部类及其 @Condition)
MemberConditions memberConditions = new MemberConditions(context, this.configurationPhase, className);
// 获取所有内部条件的匹配结果
MemberMatchOutcomes memberOutcomes = new MemberMatchOutcomes(memberConditions);
// 委托给子类决定最终结果(与、或、非逻辑)
return getFinalMatchOutcome(memberOutcomes);
}
/**
* 留给子类实现的逻辑,参数为内部所有 Condition 的匹配结果集合。
*/
protected abstract ConditionOutcome getFinalMatchOutcome(MemberMatchOutcomes memberOutcomes);
protected static class MemberMatchOutcomes {
// 全部结果
private final List<ConditionOutcome> all;
// 匹配成功的
private final List<ConditionOutcome> matches;
// 匹配失败的
private final List<ConditionOutcome> nonMatches;
}
private static class MemberConditions {
private final ConditionContext context;
private final MetadataReaderFactory readerFactory;
private final Map<AnnotationMetadata, List<Condition>> memberConditions;
// key:内部类的注解元数据;value:其上声明的所有 Condition 实例
MemberConditions(ConditionContext context, ConfigurationPhase phase, String className) {
this.context = context;
this.readerFactory = new SimpleMetadataReaderFactory(context.getResourceLoader());
// 获取这个className所有的内部类
String[] members = getMetadata(className).getMemberClassNames();
// 实例化内部类上的所有Condition
this.memberConditions = getMemberConditions(members, phase, className);
}
// 进行Condition的匹配并返回结果
List<ConditionOutcome> getMatchOutcomes() {
List<ConditionOutcome> outcomes = new ArrayList<>();
// 处理每个内部类对应的所有Condition
this.memberConditions.forEach((metadata, conditions) -> outcomes
.add(new MemberOutcomes(this.context, metadata, conditions).getUltimateOutcome()));
return Collections.unmodifiableList(outcomes);
}
}
private static class MemberOutcomes {
private final ConditionContext context;
private final AnnotationMetadata metadata;
private final List<ConditionOutcome> outcomes;
MemberOutcomes(ConditionContext context, AnnotationMetadata metadata, List<Condition> conditions) {
this.context = context;
this.metadata = metadata;
this.outcomes = new ArrayList<>(conditions.size());
for (Condition condition : conditions) {
this.outcomes.add(getConditionOutcome(metadata, condition));
}
}
private ConditionOutcome getConditionOutcome(AnnotationMetadata metadata, Condition condition) {
if (condition instanceof SpringBootCondition) {
return ((SpringBootCondition) condition).getMatchOutcome(this.context, metadata);
}
return new ConditionOutcome(condition.matches(this.context, metadata), ConditionMessage.empty());
}
/**
* 将某个内部类中所有 Condition 的匹配结果整合为一个最终结果:
* - 全部匹配才算 match
* - 否则 noMatch
*/
ConditionOutcome getUltimateOutcome() {
ConditionMessage.Builder message = ConditionMessage
.forCondition("NestedCondition on " + ClassUtils.getShortName(this.metadata.getClassName()));
if (this.outcomes.size() == 1) {
ConditionOutcome outcome = this.outcomes.get(0);
return new ConditionOutcome(outcome.isMatch(), message.because(outcome.getMessage()));
}
List<ConditionOutcome> match = new ArrayList<>();
List<ConditionOutcome> nonMatch = new ArrayList<>();
for (ConditionOutcome outcome : this.outcomes) {
(outcome.isMatch() ? match : nonMatch).add(outcome);
}
if (nonMatch.isEmpty()) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message.found("matching nested conditions").items(match));
}
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.found("non-matching nested conditions").items(nonMatch));
}
}
}
AllNestedConditions
内部逻辑很简单就不展示源码了,就是个与逻辑,全部的内部类match才算match。它的逻辑其实和这个Conditional注解一起用在某个配置类上一样,都是与逻辑。
但SpringBoot还是提供了这个类,试想一下,现在有个极其复杂的与逻辑Conditional注解组合要用在多个配置类上,我们就可以用AllNestedConditions来组合这些Conditional注解,将公共的功能抽出来作为一个共享的逻辑模块,就是一种模块化的思想,不论是还是功能熟悉还是后期维护,都更加的方便
AnyNestedCondition
只要任意一个内部类的条件匹配,就返回 match,实现的是或逻辑。是最常用的一个Condition组合工具
正如前面提到的,内部类的ConditionOutcome计算是与逻辑,所以在使用AnyNestedCondition时,建议每个内部类只写一个 @Conditional 注解
NoneNestedConditions
只有所有内部类的条件都不匹配时,才返回 match,相当于非逻辑
Report和Listener
在SpringBoot中可以通过如下配置,开启Condition的匹配详情日志。其对于排查Condition未生效的问题非常有帮助,是调试 SpringBoot 自动装配机制的重要手段。其原理主要依赖于ConditionEvaluationReport(ConditionOutcome缓存)和ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener(ConditionOutcome日志打印)
logging:
level:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging: debug
ConditionEvaluationReport
在 Spring Boot 中,所有的 Condition 实现类都继承自抽象类 SpringBootCondition。其中:
- 各个子类通过实现
getMatchOutcome()模板方法,完成具体的匹配逻辑判断,并生成标准化的ConditionOutcome(用于描述匹配结果及原因) SpringBootCondition会将这些ConditionOutcome缓存到ConditionEvaluationReport这个单例bean中
这个 ConditionEvaluationReport 用于汇总记录所有条件的匹配结果。SpringBoot 的日志监听器(ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener)正是基于这个 bean,在日志级别为 debug 时,输出详细的自动配置条件匹配情况
ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
这是一个配置在 spring.factories 里的 ApplicationContextInitializer,启动时会往容器里注册一个 ConditionEvaluationReportListener,专门监听 ContextRefreshedEvent 和 ApplicationFailedEvent 事件
一旦这两个事件有一个触发,它就会根据配置的 logLevelForReport(默认是 DEBUG)把所有Condition匹配情况打印出来。打印的数据来自 ConditionEvaluationReport 这个 Bean 里缓存的内容,也就是每个配置类的@Conditional 条件到底有没有命中的原因
Condition触发机制
ConditionEvaluator
ConditionEvaluator 是匹配某个配置类或 @Bean 方法上 Condition 条件注解的核心入口。它依据传入的 ConfigurationPhase 参数来判断当前所处的处理阶段( 解析配置类 或 注册 Bean 阶段)
其核心方法shouldSkip逻辑如下:
- 实例化并排序该元素上声明的所有
Condition类 - 匹配当前phase或不存在phase 的
Condition- 匹配过程中,只要有一个
Condition不满足,即返回true表示需要跳过,该元素将不会被进一步处理(不再解析配置或注册Bean)
- 匹配过程中,只要有一个
class ConditionEvaluator {
public boolean shouldSkip(@Nullable AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, @Nullable ConfigurationPhase phase) {
// 没有@Conditional注解,则表示不需要skip
if (metadata == null || !metadata.isAnnotated(Conditional.class.getName())) {
return false;
}
// 解析phase,决定当前配置类是在哪个阶段应用的Condition(解析阶段 or 注册bean阶段)
if (phase == null) {
if (metadata instanceof AnnotationMetadata &&
ConfigurationClassUtils.isConfigurationCandidate((AnnotationMetadata) metadata)) {
return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION);
}
return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);
}
List<Condition> conditions = new ArrayList<>();
for (String[] conditionClasses : getConditionClasses(metadata)) {
for (String conditionClass : conditionClasses) {
// 实例化Condition
Condition condition = getCondition(conditionClass, this.context.getClassLoader());
conditions.add(condition);
}
}
// 根据@Order排序Condition
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(conditions);
for (Condition condition : conditions) {
// 判断 Condition 的作用阶段
ConfigurationPhase requiredPhase = null;
if (condition instanceof ConfigurationCondition) {
requiredPhase = ((ConfigurationCondition) condition).getConfigurationPhase();
}
// 不存在phase(即不论什么作用阶段,都需要进行匹配)或phase等于指定的阶段才进行匹配
// 但凡任意一个Condition匹配失败,则返回true,表示需要skip
if ((requiredPhase == null || requiredPhase == phase) && !condition.matches(this.context, metadata)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
TrackedConditionEvaluator
这是 Spring 在注册配置类 Bean 之前,用于评估 @Conditional 是否匹配的辅助工具。与普通 ConditionEvaluator 不同,它特殊的支持了根据导入当前配置类的其他配置类(即 importedBy)的Condition匹配情况,来共同决定当前类是否应跳过注册(skip)
其核心方法shouldSkip是一个基于 记忆搜索优化 + 剪枝的回溯算法(我们将参数configClass想象为当前节点,其importedBy想象为子节点,形成一棵由导入关系构成的树形结构),其核心逻辑为:
- 某个节点其任意一个importedBy不需要skip时,转而直接判断当前节点配置类的
Condition决定其是否skip(break进行剪枝,不再判断其它importedBy的skip情况) - 某个节点所有importedBy都skip时,则不再判断当前节点的
Condition,直接确认skip
private class TrackedConditionEvaluator {
private final Map<ConfigurationClass, Boolean> skipped = new HashMap<>();
public boolean shouldSkip(ConfigurationClass configClass) {
Boolean skip = this.skipped.get(configClass);
if (skip == null) {
// 若该配置类是通过 @Import 导入的,优先判断导入它的配置类是否应被skip
if (configClass.isImported()) {
boolean allSkipped = true;
for (ConfigurationClass importedBy : configClass.getImportedBy()) {
// 回溯
if (!shouldSkip(importedBy)) {
// 但凡有一个导入者不需要skip,转而判断自身并剪枝
allSkipped = false;
break;
}
}
if (allSkipped) {
// 所有导入者都被跳过,则让当前配置类直接skip
skip = true;
}
}
if (skip == null) {
// 判断自己的Condition,决定是否需要skip
skip = conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);
}
// 缓存优化
this.skipped.put(configClass, skip);
}
return skip;
}
触发地点
前置文章:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor解析配置类
ConditionEvaluator触发
ConfigurationClassParser#processConfigurationClass
所有配置类解析的起点,此处触发
ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION阶段的Condition判断ConfigurationClassParser#doProcessConfigurationClass:
解析配置类上的
@ComponentScan注解时触发。该注解所扫描的组件将直接注册为 Bean,此阶段对应ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEANConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod
在注册配置类中的
@Bean方法时触发。每个BeanMethod都根据其方法上的Condition进行匹配,为ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN阶段
TrackedConditionEvaluator触发
ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass
在注册配置类内部所有 Bean(包括
@Bean方法、通过@Import引入的ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar、以及@ImportResource导入的 XML Bean)前,会调用TrackedConditionEvaluator判断该配置类是否整体满足Condition,从而决定是否跳过整个类的 Bean 注册流程。
测试用例
Condition组合-AnyNestedCondition
这是一个组合Condition(或逻辑)的测试用例,只要condition.or.enable=true或condition.or.use=yes任意条件满足,则可注册C对象到容器中
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class NestedOrConditionDemo {
static class OrCondition extends AnyNestedCondition {
public OrCondition() {
super(ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);
}
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "condition.or.enable", havingValue = "true")
static class PropertyOrEnable{}
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "condition.or.use", havingValue = "yes")
static class PropertyOrUse{}
}
public static class C{
public void init(){
System.out.println("NestedOrConditionDemo$C initialized");
}
}
@Bean(initMethod = "init")
@Conditional(OrCondition.class)
public C buildC(){
return new C();
}
}
配置
condition:
or:
enable: "false"
use: "yes"
TrackedConditionEvaluator测试
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(D.class)
public class ImportTrackedConditionDemo {
}
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(A.class)
class A{}
@Import(A.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(B.class)
class B{}
@Import(B.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(C.class)
class C{}
@Import(value = {C.class, A.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(D.class)
class D{}
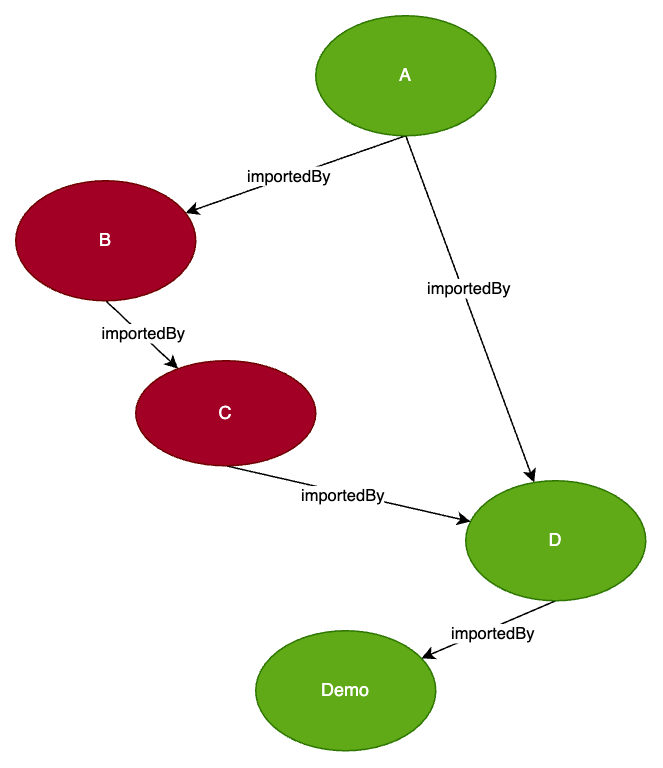
这个测试用例用来验证 TrackedConditionEvaluator#shouldSkip 的执行逻辑,能完整模拟它的skip机制,并覆盖到 记忆搜索、剪枝等优化逻辑。A对象的整个importBy链路图如下,其整体流程可以总结为:
- C 的
Condition不满足(@ConditionalOnBean 没匹配上),直接标记为 skip - B 是被唯一一个C @Import 的,发现 C 被 skip 后,B 自己也不再判断
Condition,直接也 skip - 然后判断 A,因为 A -> B 这条链断了,就继续看 A -> D
- 由于D的结果已被缓存为不被skip,所以A转而判断自身的
Condition,最终得到不需要skip的结果
- 由于D的结果已被缓存为不被skip,所以A转而判断自身的
打开condition debug,也能从日志看出:
- A 和 D 都走了
Condition匹配逻辑 - C 被判定不匹配
- B 根本没触发
Condition判断
A matched:
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean (types: site.shanzhao.soil.spring.config.A; SearchStrategy: all) did not find any beans (OnBeanCondition)
D matched:
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean (types: site.shanzhao.soil.spring.config.D; SearchStrategy: all) did not find any beans (OnBeanCondition)
C Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnBean (types: site.shanzhao.soil.spring.config.C; SearchStrategy: all) did not find any beans of type site.shanzhao.soil.spring.config.C (OnBeanCondition)
感想
本来只是打算简单写写几个常见的 @Conditional 注解实现,结果一深入源码,才发现背后藏着这么多细节。不知不觉间内容越写越多,也越写越上头
让我感慨的是,这不过是 Spring 中一个小小的功能点,却被设计得这么精巧。像灵活的条件组合机制,几乎能支持任何类型的 Condition 实现;又比如通过模板方法模式抽象出的 ConditionOutcome,不仅解耦了逻辑判断,还天然支持调试信息输出;再比如 importedBy 链路配合 TrackedConditionEvaluator 做到的递归判断与算法优化,每个功能看起来简单,但组合在一起就是工程化的思路体现
写到最后,不得不感叹一句:麻雀虽小,五脏俱全。只能说越看越觉得厉害,代码之路任重而道远啊